
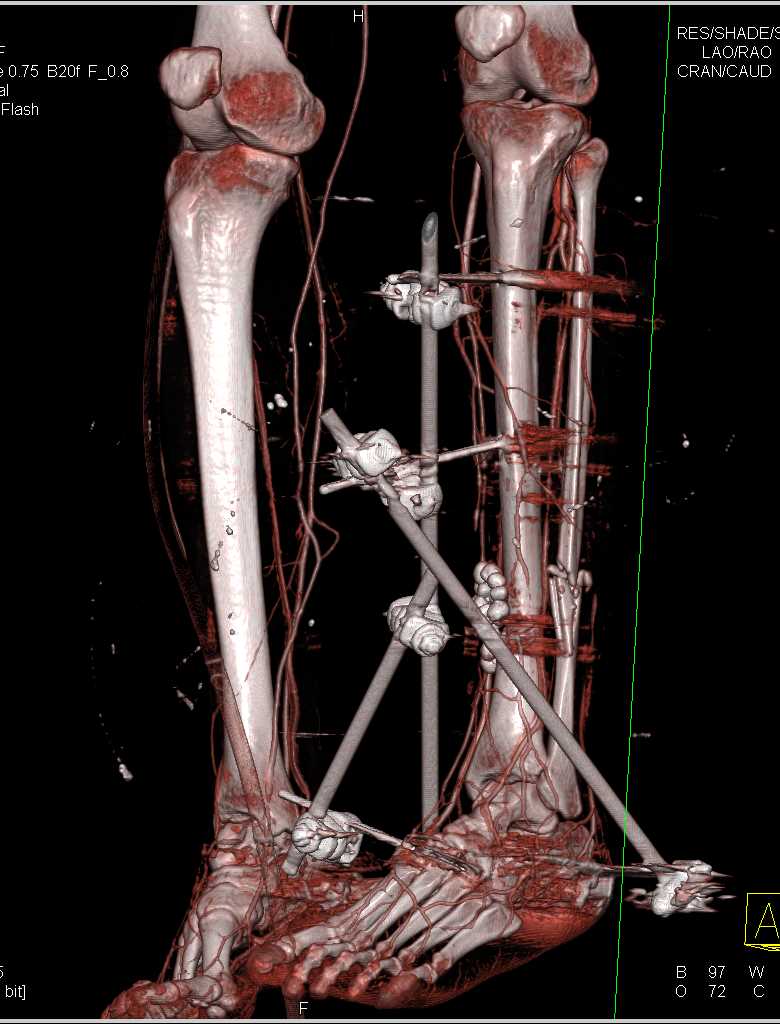
If a cast or splint isn’t possible because of the nature of the injury, an ‘external fixator’ may be considered where pins are inserted above and below the joint. Once swelling has gone down and the soft tissues recover in days or weeks to come, the incisions are closed.
#Tibia and fibula fracture skin#
This condition requires emergency surgery called a fasciotomy, where vertical incisions are made to release the skin and muscle coverings. Occasionally soft tissue swelling may be so severe that it inhibits blood supply to both the leg and foot, a condition referred to as compartment syndrome. In these circumstances, early surgical treatment is required to cleanse the fracture surfaces and soft tissue surrounding the injury to prevent infection.

If there is an open wound and the skin is broken there is great concern that the fracture may be exposed to bacteria that might cause infection. (2005) states that the trick to good treatment is to ensure the bone heals in the correct position. In order for adequate healing, both the fracture and the surrounding soft tissue damage should be treated at the same time, with or without surgery. Due to the possibility of soft tissue damage, an orthopaedic surgeon would also look for signs around the fracture and include this in the management plans for the fracture. The soft tissues surrounding the tibia and fibula such as skin, muscle, nerves, etc may also be injured at the time of the impact. (2008) state that the aim of treatment is to achieve a functional limb and to minimise physical, social and psychological morbidity.Ĭorrect identification and management of injuries such as a tibia and fibula fracture is important to ensure that the limb functioning such as strength, motion and stability is fully restored and also lessen the risk of arthritis. In the journal ‘Tibial non-union: a review of current practice’, Moulder et al. Some of the symptoms include pain on the weight bearing leg, bruising of the injured area, tenderness around the knee and limited bending of the knee and/or ankle due to bleeding within the joint, possible deformity around the knee, pale and/or cool foot due to poor blood supply and numbness or an unusual sensation around the foot which indicates possible nerve injury or excessive swelling within the leg. Ī fracture to the tibia and fibula can cause multiple injuries such as bone damage and soft tissue damage. Special procedures including temperature tests are used to assess blood supply to the injured leg. Once the clinical examination is complete, X-Rays and sometimes CT scans of the knee, tibia and fibula and ankle are taken to determine the exact location and severity of the fracture. The physician will make note of any temperature drops (due to a lack of blood to limb) or altered or lack of sensation which may point to further complications During further examination an assessment will be made of the nerve and blood supply by visually inspecting and palpating the extremities.
#Tibia and fibula fracture professional#
If you need assistance with writing your nursing essay, our professional nursing essay writing service is here to help! Find out moreĪfter a history and initial set of observations having been recorded, the physician will then inspect the injury more closely. Further investigation for a patient medical history and and any secondary injuries or complaints are also determined at this time. The physician should initially examine the patient for oedema (swelling), ecchymosis (bruising), and the point of tenderness. The clinical examination includes questions such as what events were leading up to the injury and symptoms that are present to the patient. The diagnosis of a tibia and fibula fracture is determined by clinical examination and imaging resources. Fractures of the tibia can also involve the tibial plateau, tibial tubercle, tibial eminence, proximal tibia, tibial shaft, and tibial plafond. The tibia is the main, weight bearing bone of the lower leg and when broken, the fibula that runs alongside the tibia, is generally broken as well because the force of the break is transmitted along the interosseous membrane of the fibula. Sarah’s boot top fractured occurred in exactly that way. They are often associated with skiing due to wearing tightly secured boots that come up to the mid-shaft calf. Share this: Facebook Twitter Reddit LinkedIn WhatsAppĪ ‘boot top’ fracture is an injury to the lower leg caused by high impact trauma.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
